5 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance
In this paper the authors discuss some mechanisms of antibiotic resistance such as changing the antibacterial agents uptake and biofilm formation as well as a wide range of approaches such as developing new generations of antibiotics. To better illustrate the temporal variation of antibiotic resistance on the MPs and in the receiving waters the ternary plots were used to analyze dynamic variation of genes within 4 weeks after MPs were relocated to the new receiving waters.
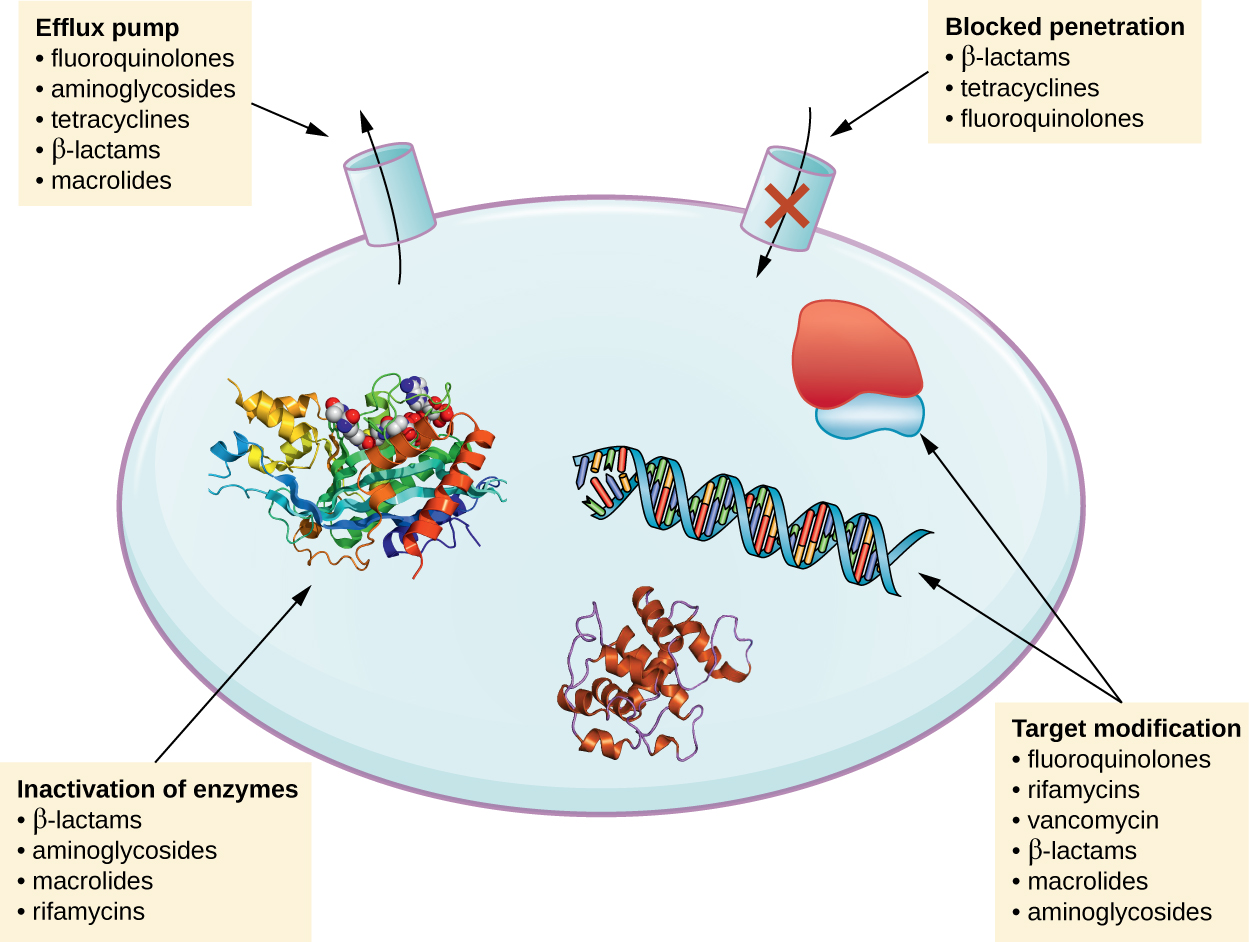
11 7 Mechanisms For Resistance Biology Libretexts
These bacteria can.
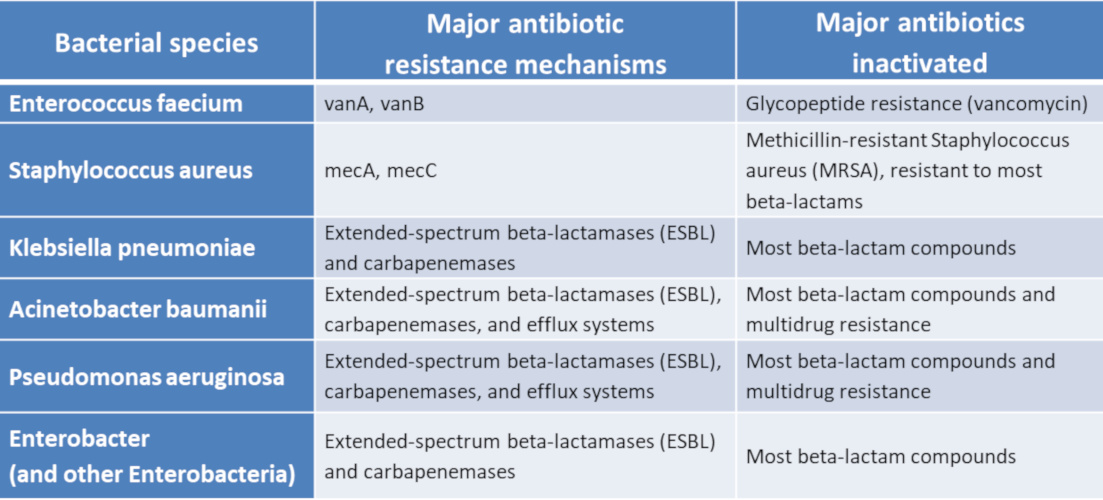
. Mechanisms for the development of resistance. The species of the greatest clinical importance are Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. Resistance Mechanisms Defense Strategies Resistance Mechanisms Defense Strategies Description.
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer layer membrane that protects them from their environment. Aeruginosa depends primarily on multiple intrinsic and acquired antibiotic resistance mechanisms including the biofilm-mediated formation of resistant and. A growing list of infections such as.
Resistance to even one antibiotic can mean serious problems. Infections caused by resistant bacteria may require more care as well as alternative and more expensive antibiotics which may have more severe side effects. The acquisition of drug resistance by P.
This review highlights the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in P. Aeruginosa is a recently characterized mechanism which includes biofilm-mediated resistance and formation of multidrug-tolerant persister cells and is responsible for recalcitrance and relapse of infections. Further studies ought to be dedicated to interaction mechanisms of ARGs MGEs and their bacterial.
Antimicrobial agents play a key role in controlling and curing infectious disease. Antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest threats to global health food security and development today. This study discusses the impact of antibiotic resistance as a persistent.
Antimicrobial-resistant infections that require the use of second- and third-line treatments can harm patients by causing serious side effects such as organ failure and. The clinical importance of the genus Enterococcus is directly related to its antibiotic resistance which contributes to the risk of colonization and infection. Antimicrobial agents use different mechanisms against bacteria to prevent their pathogenesis and they can be classified as bactericidal or bacteriostatic.
New resistance mechanisms are emerging and spreading globally threatening our ability to treat common infectious diseases. Antibiotic resistance can affect anyone of any age in any country. Restrict access of the antibiotic.
Germs restrict access by changing the entryways or limiting the number of entryways. Antibiotic resistance often referred to as antimicrobial resistance AMR although this term covers anti-virals anti-fungals and other products can occur when antibiotics are present in concentrations too low to inhibit bacterial growth triggering cellular responses in the bacteria that. Resistant bacteria survive in the presence of the antibiotic and continue to multiply causing longer illness or even death.
Read more in the factsheets about antimicrobial resistance. Soon after the discovery of the first antibiotic the challenge of antibiotic resistance commenced. Although the resistance characteristics of these two species differ in important ways they can generally.
It is estimated that the number of deaths due to antibiotic resistance will exceed ten million annually by 2050 and cost approximately 100 trillion USD worldwide 123Antibiotic resistance arises when bacteria are able to survive an exposure to antibiotics that would normally kill them or. In addition adaptive antibiotic resistance of P. Antibiotic resistance is an urgent and growing global public health threat.
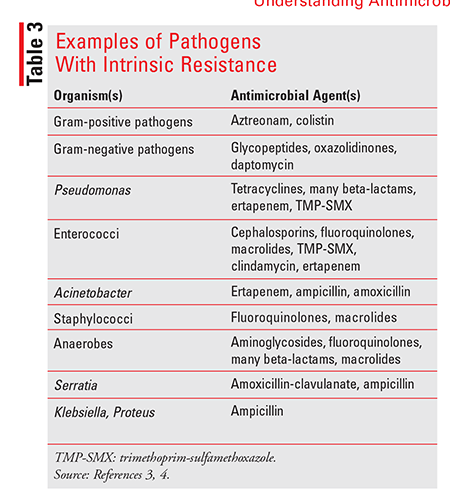
Understanding Antimicrobial Resistance

What Are The Mechanisms Of Antimicrobial Resistance

Antibiotics Antibiotic Resistance And Environment Encyclopedia Of The Environment
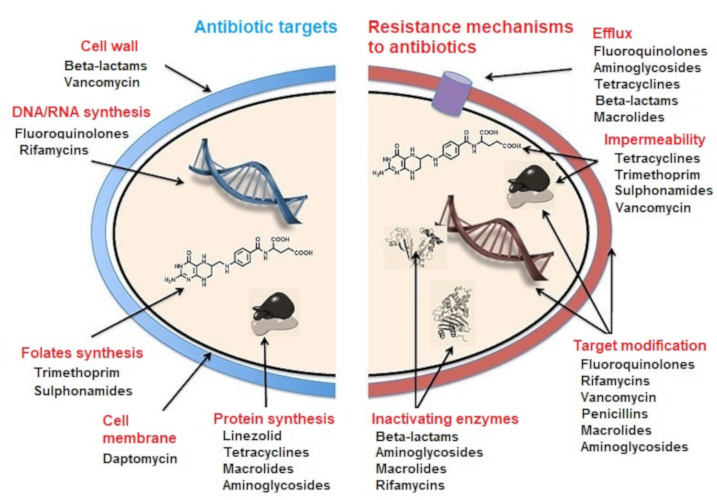
Antibiotics Antibiotic Resistance And Environment Encyclopedia Of The Environment

Mechanism Of Action Of Antibiotics Download Scientific Diagram

Antimicrobial Resistance Phenomenon Antimicrobial Resistance Phenomena Antimicrobial
0 Response to "5 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance"
Post a Comment